Value Creation
Stakeholder Engagement
Active and consistent engagement with stakeholders is essential to foster meaningful relationships based on mutual trust, accountability and transparency. At Kotak Mahindra Group, we seek to engage with our stakeholders regularly. Our engagement strategy is designed with the goal of recognising the stakeholders' present and future needs and expectations. The outcome of this engagement forms the basis of our approach towards organisational strategy as well as risk management and helps enhance customer experience.
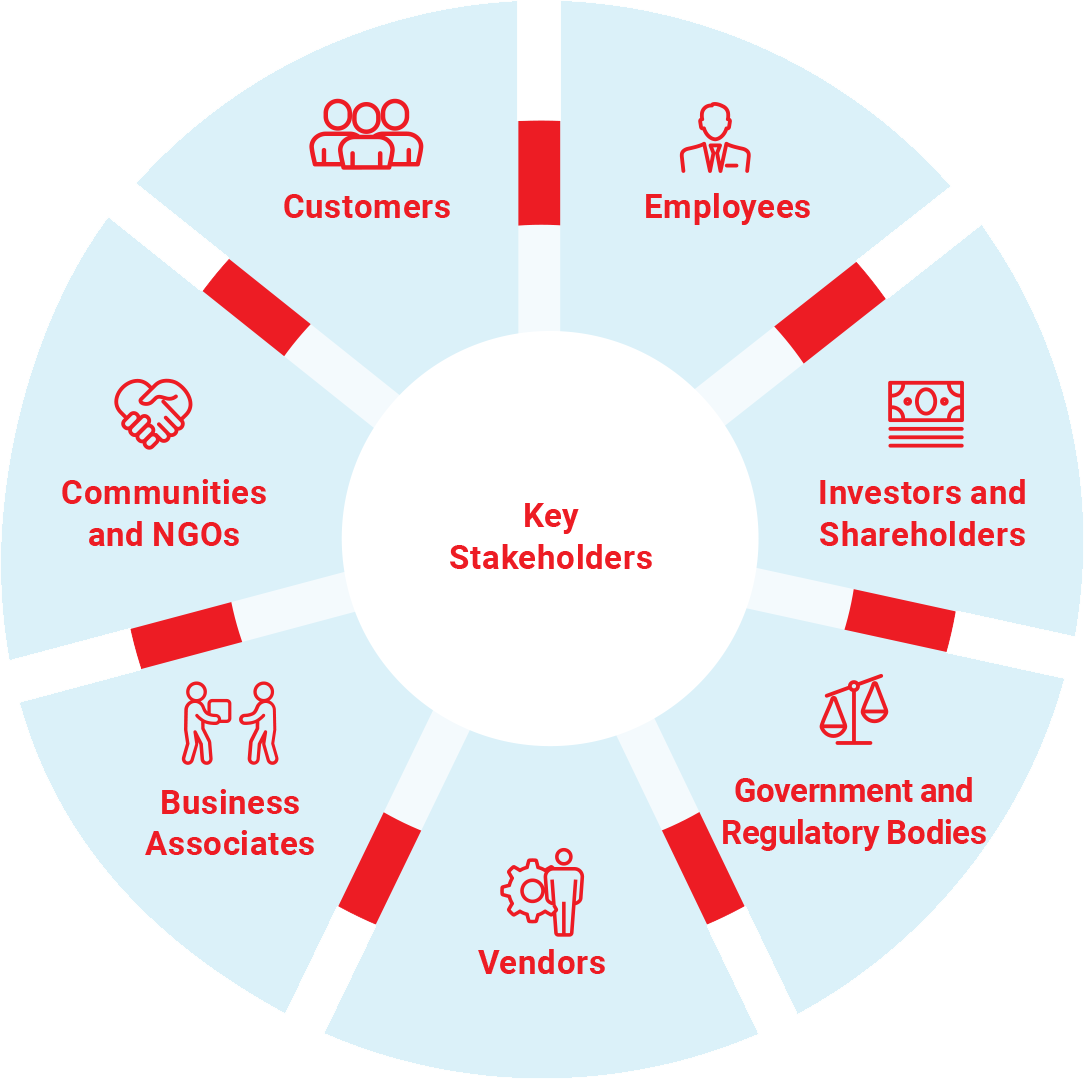
In line with our engagement strategy, we have identified seven critical stakeholder groups that are seen as being the most important for our business. The strategy is tailored for each stakeholder group as detailed on Read more, the medium we have adopted for engaging with them, the frequency of such engagements and the key topics on which we engage. The table also provides the activities that we undertake based on stakeholder inputs.
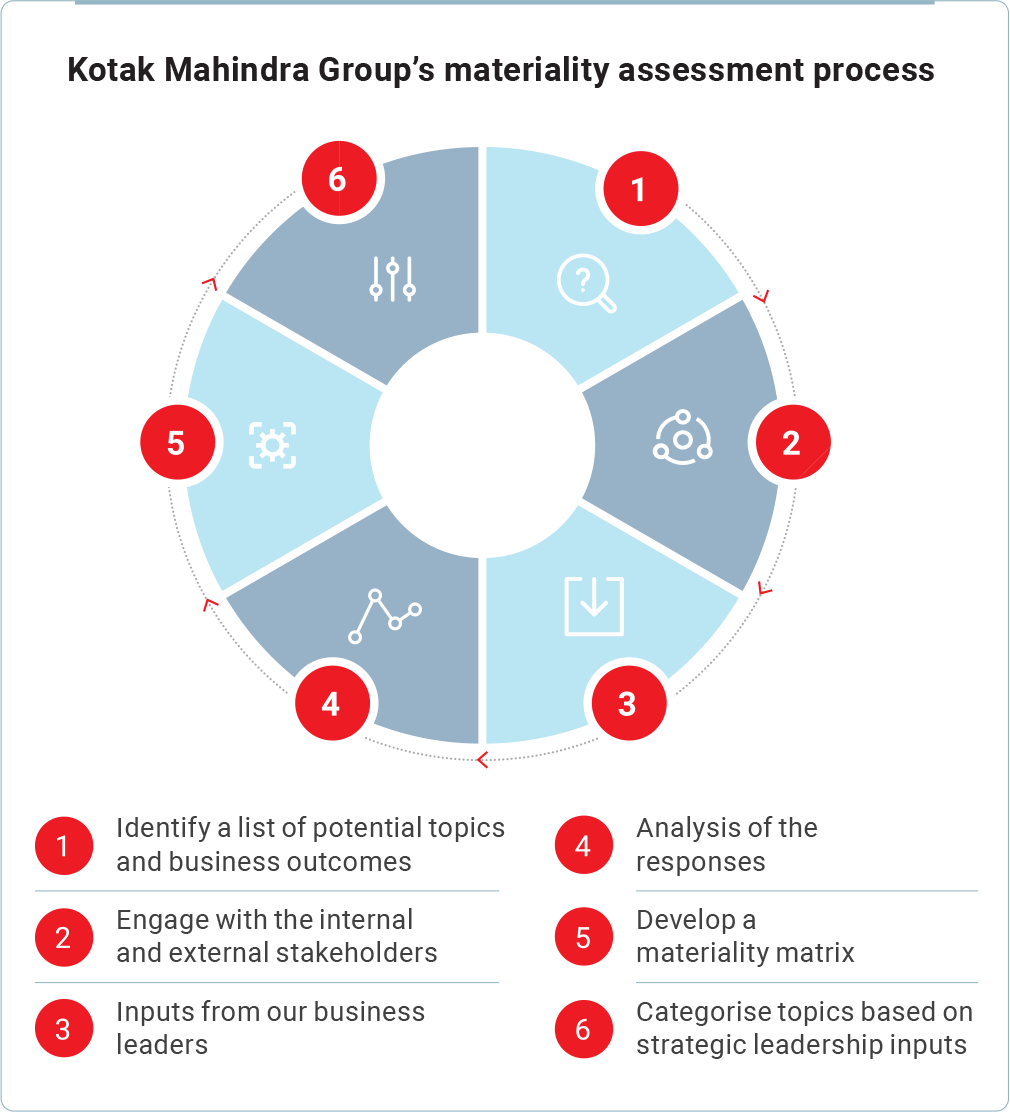
Materiality Assessment Exercise1
Material topics refer to topics that represent the organisation’s most significant impacts on the economy, environment and people, including impacts on their human rights.2 We adopt the principle of materiality to categorise topics for disclosure and integration into our ESG strategy. In FY 2021-22, we carried out a systematic materiality assessment exercise in compliance with GRI principles.
An exhaustive list of material topics was identified on the basis of the material themes suggested by globally acknowledged sustainability standards and guidelines for the financial sector as well as a peer study. The identified topic universe was also developed in line with the impacts that arise as a result of our business activities. These included impacts that could arise from our products and services offered to clients across industry sectors and our operations.
We identified a list of key business outcomes that were used to gauge the impacts of material topics on business. Our senior leadership was involved in the review of the range of potential effects that the material topics could have on the identified business outcomes. An online survey mechanism was used to gather and consolidate perspectives from a diverse set of important internal and external stakeholders.
1GRI 3-1 | 2As defined in the GRI Universal Standards 2021
We sought views from the stakeholders to rank the topics based on their importance which helped us to determine the relative relevance of the identified material topics.
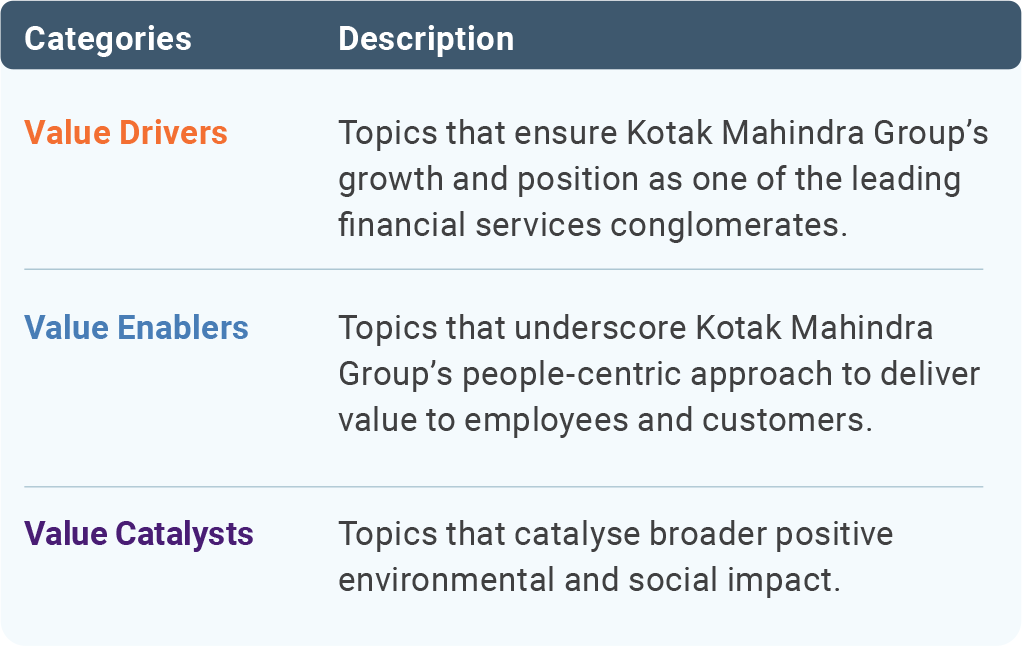
With the help of the exercise's results, we defined and grouped our major ESG emphasis areas, i.e. material topics into value drivers, value enablers and value catalysts, as follows: environmental sustainability’ and ‘Minimising risk impact of climate change due to investments/advances’ were categorised as value drivers and ‘Promoting financial inclusion’ as a value enabler.
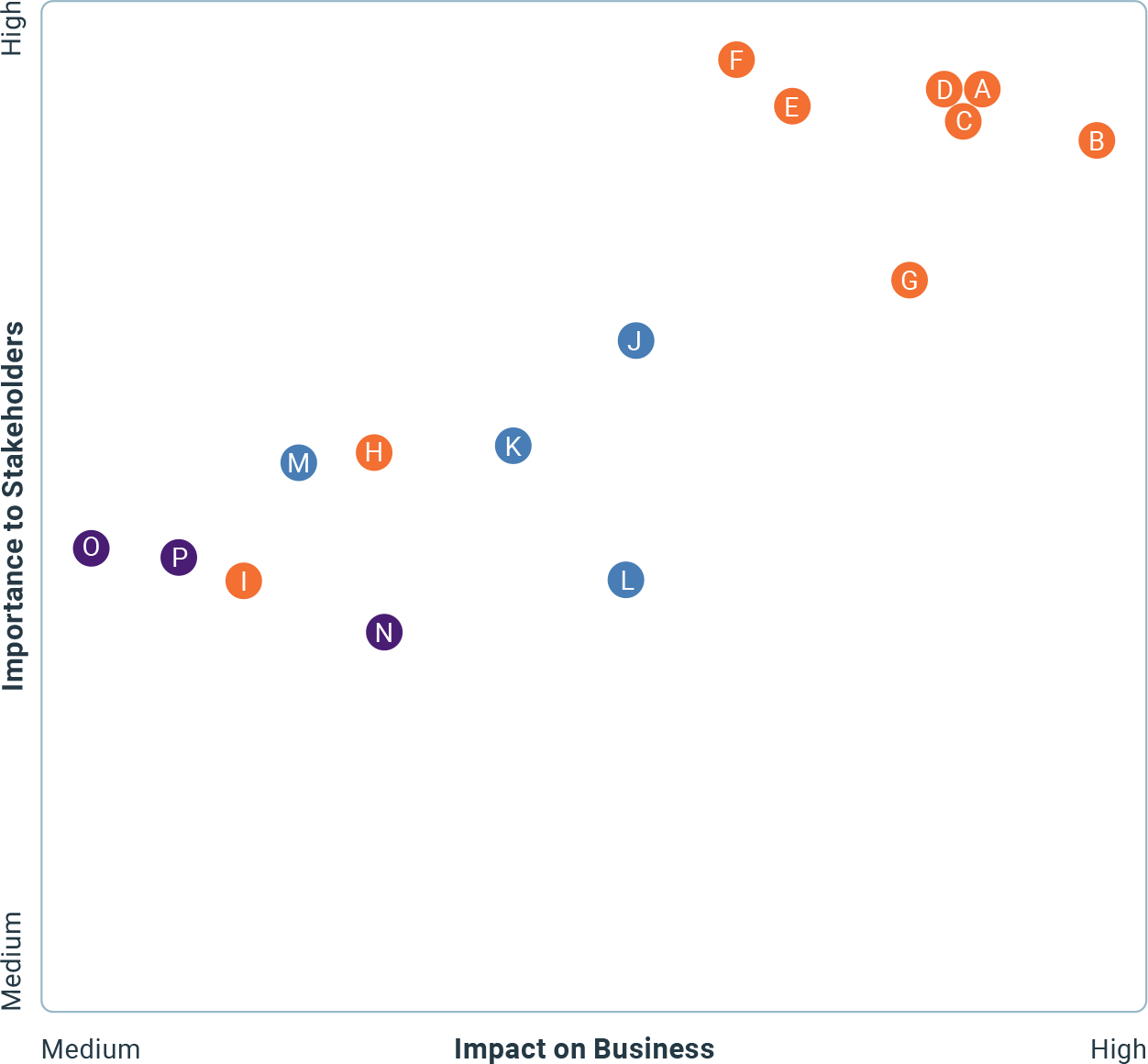
Materiality Matrix
REVIEW OF MATERIALITY ASSESSMENT
We have set a biennial frequency to undertake a materiality assessment, with the next exercise planned for FY 2023-24, which would be in line with the materiality approach outlined in GRI 2021 standards. Even as an assessment is planned biennially, the material topics are reviewed on an annual basis to ensure relevance with our business and for staying up to date with emerging sector issues.
For the reporting period, we have undertaken a review of the materiality exercise conducted in the previous reporting period in consultation with key internal stakeholders. The exercise included revalidation of underlying identified business outcomes that informed the materiality exercise. The review concluded that the list of business outcomes, and by extension the material topics remain largely unchanged. It may be noted that the scope of one identified business outcome has expanded due to additional internal controls and monitoring processes that were put in place post the conclusion of the materiality exercise last year.
The materiality assessment exercise that would be undertaken in FY 2023-24 shall be in line with the GRI Universal Standards 2021. This periodic stakeholder engagement process would help us in aligning our material topics with the evolving business ecosystem and enable us to strengthen our business strategy.
Value Drivers
- Enhancing customer experience
- Corporate governance
- Ethical business processes
- Regulatory compliance
- Data security
- Customer data privacy
- Brand and reputation
- Financing with a focus on environmental sustainability
- Minimising risk impact of climate change due to investments/ advances
Value Enablers
- Promoting employee health, safety and well-being
- Promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion amongst employees
- Enabling learning, development, and an open work culture for employees
- Promoting financial inclusion
Value Catalysts
- Contributing to development of regulations and policies
- Minimising environmental impact of operations
- Community well-being
Table 1. Kotak Mahindra Group’s Material Topics and some key performance indicators are covered in this Report1
| Material Topic | Description | Rationale for materiality and management approach2 | Section of the Report covering management approach2, 3 | Our performance4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
VALUE DRIVERS |
||||
Corporate governance |
Covers Board and management effectiveness and integrity, remuneration policies and practices, audit and financial reporting practices that promote high level of transparency, accountability, and Board oversight. |
Failure to adhere to good governance practices could pose significant risks to operations, financial performance, and ultimately long-term success for the organisation. This could result in financial penalties, reduction in access to capital and reduced share price. |
|
|
Enhancing customer experience |
Enhance customer satisfaction via product innovation, efficient processes, digital solutions, easy access to products and services, fair marketing practices and efficient complaint resolution. |
Enhancing customer experience and satisfaction can help Kotak improve customer retention, increase revenue, differentiate the Bank from competitors, build a strong brand image, increase customer base and reduce costs. |
|
|
Ethical business processes |
Ethical conduct of business, including in areas such as taxation and accounting, anti-corruption, anti-money laundering, anti-competitive practices, insider trading and intellectual property issues. |
Ethical business practices can present opportunities by building a strong reputation and brand, managing risks, attracting and retaining employees and customers. |
|
|
Regulatory compliance |
Adherence to laws, regulations and guidelines |
In an ever-evolving regulatory landscape it is imperative for organisations to ensure compliance on current and emerging regulations. Failure to keep abreast with the dynamic policy and regulatory landscape can lead to litigation, regulatory and reputational risks. |
|
|
Data security |
Prevent and address IT system failures and major cybersecurity incidents. |
Data security is a significant risk for organisations handling large volumes of sensitive financial and personal data. Lack of robust data privacy systems can result in financial penalties, increased legal fees arising from lawsuits and reduction in customer retention. |
|
|
Customer data privacy |
Measures taken to ensure safe and secure use and maintenance of customers’ data. |
Data breaches or unauthorised access to customer data could lead to legal liabilities, including lawsuits from customers, regulatory investigations, financial penalties and damage to brand and reputation leading to reduction in customer retention. |
|
|
Brand and reputation |
Build and enhance the reputation and brand to enable stakeholder confidence. |
Positive brand and reputation helps attract and retain customers and other stakeholders such as investors, employees and shareholders. Positive reputation can also help dampen impacts of macroeconomic risks. |
|
|
Financing with a focus on environmental sustainability |
Identify and leverage sustainable financing opportunities with positive environmental impact. Offer products and services with a focus on sustainability. |
Environmentally conscious financing could help build trust among environmentally conscious stakeholders, reduce exposure and losses arising from climate risks and support transition to a low carbon economy. |
|
|
Minimising risk impact of climate change due to investments/ advances |
Mitigate climate risks by managing the investment and advances portfolio mix to minimise expected losses resulting from climate change. |
Mitigating climate risks by managing the portfolio mix of investment and advances can lead to new green and climate resilient financing opportunities. |
|
|
VALUE ENABLERS |
||||
Promoting employee health, safety, and wellbeing |
Provide a safe workplace and proactively address health and safetyrelated concerns through trainings, safety drills, ergonomics, insurance, etc. |
Promoting employee health, safety, and wellbeing enhances employee productivity and minimises absenteeism, employee turnover and hiring costs. |
|
|
Promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion amongst employees |
Provide equal and fair remuneration and advancement opportunities to all employees. Run programmes and activities to promote workforce diversity and inclusion. |
Promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) amongst employees can provide numerous benefits including increased innovation and creativity, enhanced reputation, better risk management, and compliance with regulations. By prioritising DEI, banks can create a positive work environment that supports overall business goals and contributes to its long-term success. |
|
|
Enabling learning, development, and an open work culture for employees |
Initiatives to improve collaboration and mutual respect, towards creating an open and approachable work culture. Conduct training and leadership development programmes. |
Enabling learning, development, and an open work culture for employees is an opportunity to increase employee engagement, retention and performance, decreased hiring costs, enhance reputation, attract top talent, and gain a competitive advantage. |
|
|
Promoting financial inclusion |
Ensure the availability of and access to financial services for unbanked and underbanked people. |
Promoting financial inclusion is an opportunity to access new markets, generate new revenue streams, improve reputation, and also contribute to the economic development. |
|
|
VALUE ENABLERS |
||||
Contributing to development of regulations and policies |
Provide views and ideas to assist the development of regulations and policies for building sustainable practices in the industry. |
Contributing to the development of regulations and policies could be an opportunity to demonstrate commitment to responsible governance, reduce regulatory risk, enhance collaboration and improve brand and reputation. |
|
|
Minimising environmental impact of operations |
Optimise energy and water use, along with reducing greenhouse gas emissions and waste, and investments in environmentally sustainable programmes. |
Minimising environmental impact can help meet regulatory requirements, enhance reputation, reduce costs, increase revenue and generate new business opportunities. |
|
|
Community wellbeing |
Programmes to address the developmental needs of communities through CSR (social service initiatives). |
By investing in community development, organisations can make a positive impact on the communities and contribute to the long-term sustainability of business operations. This can result in stronger relationship with communities. |
|
|
Note
Each topic is marked with | or | to indicate (  ) risk or (
) risk or (  ) opportunity followed by a column on the rationale of identifying as such and our approach to addressing
it, as required by BRSR.
) opportunity followed by a column on the rationale of identifying as such and our approach to addressing
it, as required by BRSR.
1GRI 3-2, GRI 2-25 | 2BRSR, Section A, Question 24 describing rationale for identifying a material topic as risk or opportunity, approach to adapt or mitigate and the financial implications of the risk or opportunity | 3GRI 3-3 | 4The performance is indicated for the bank wherever it is not mentioned specifically. The static figures mentioned in the KPIs are as on 31st March, 2023. The period figures mentioned are for FY 2022-23. | 5GRI 2-27
2BRSR, Section A, Question 24 describing rationale for identifying a material topic as risk or opportunity, approach to adapt or mitigate and the financial implications of the risk or opportunity | 3GRI 3-3 | 4The performance is indicated for the bank wherever it is not mentioned specifically. The static figures mentioned in the KPIs are as on 31st March, 2023. The period figures mentioned are for FY 2022-23